Peritoneal Dialysis In India
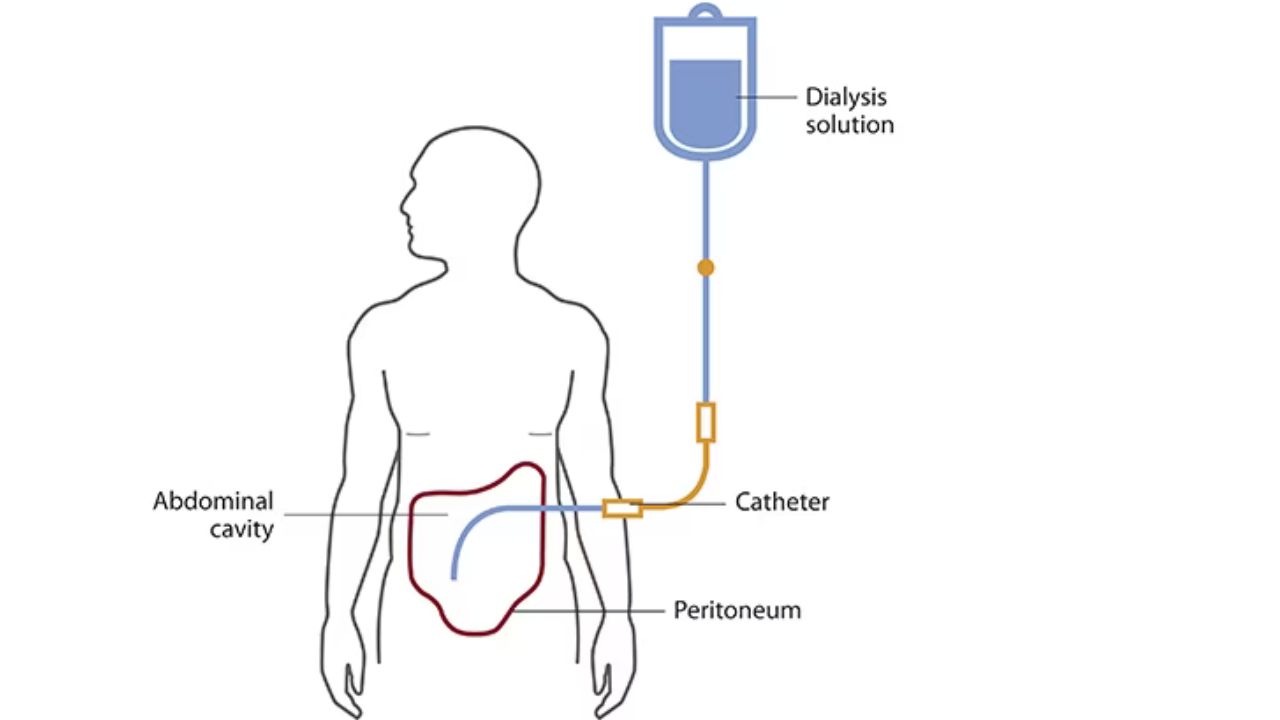
Peritoneal Dialysis In India (PD) is a vital treatment for those with end-stage renal disease. It helps remove waste and excess fluid when the kidneys fail. During the procedure, dialysis fluid is introduced into the abdomen through a catheter. The peritoneum, the lining of the abdomen, acts as a filter to clean the blood. After a set period, the fluid, now filled with waste, is drained out.
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD): CAPD is done manually. Patients connect a tube to their catheter and fill their abdomen with dialysis fluid from a bag. This is repeated three times daily. Each session takes 30 to 40 minutes.
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD): APD involves a machine, or cycler, that performs multiple exchanges automatically. The machine fills and drains the fluid while the patient sleeps. This process typically lasts 10 to 12 hours overnight.
When is Peritoneal Dialysis Needed?
Patients with chronic kidney disease at end-stage renal disease require dialysis. This can be due to conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or glomerulonephritis. PD offers flexibility and less disruption compared to hemodialysis.
Ideal Candidates for Peritoneal Dialysis
PD is suited for individuals who cannot handle the rapid fluid changes of hemodialysis. It is also ideal for those who want a flexible lifestyle and wish to retain some kidney function.
Who Should Avoid Peritoneal Dialysis?
Not everyone is a good candidate for PD. It is not recommended for people with extensive abdominal scarring, hernias, or inflammatory bowel disease. Those who lack sufficient support or are unable to care for themselves may also not benefit from PD.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Doctors determine the need for PD through blood and urine tests, kidney biopsies, and imaging like CT scans or MRIs. They also use the Peritoneal Equilibrium Test (PET) to assess the effectiveness of dialysis and make necessary adjustments.
Possible Complications
PD can lead to weight gain due to the caloric content of the dialysis fluid. It may also cause infections at the catheter site or in the abdominal lining. Additionally, prolonged use might reduce its effectiveness, requiring a switch to hemodialysis. Hernias are another risk, caused by prolonged fluid retention.
In summary, peritoneal dialysis is a flexible and effective option for managing kidney failure. However, it requires careful monitoring to manage potential risks and complications.