Heart Blockage Treatment in India
Understanding Heart Blockage
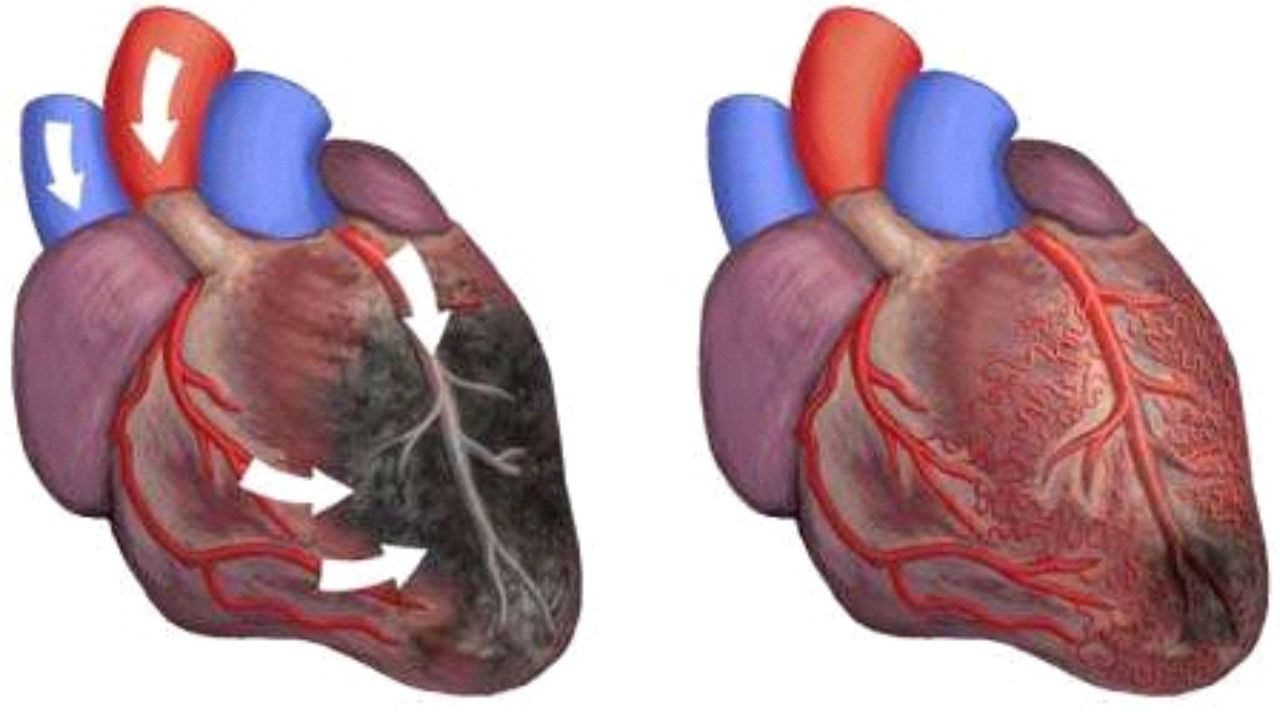
Heart blockage happens when an abnormal heart rhythm slows the heart’s beating. The heartbeat is driven by an electrical signal from the sinoatrial node at the top of the right atrium. This signal travels through the atria to the atrioventricular node, prompting the heart to contract and pump blood. When this signal is delayed or interrupted, heart block occurs, also known as atrioventricular block (AV block).
Types of Heart Blockage
- First-Degree Heart Blockage: This type slows the electrical signals as they move from the atria to the ventricles, making it the least severe form.
- Second-Degree Heart Blockage: Electrical impulses are delayed until a beat fails to reach the ventricles. It is divided into two types:
- Mobitz Type I: Electrical signals progressively slow between each beat, eventually causing the heart to drop a beat.
- Mobitz Type II: There is no fixed pattern of electrical signals reaching the ventricles from the atria.
- Third-Degree Heart Blockage: This is the most severe form. Electrical signals do not reach the ventricles, triggering ventricular escape beats, which are typically slow and can be fatal if untreated.
Causes of Heart Blockage
Heart block can be congenital or acquired. Congenital heart block may result from an autoimmune disease passed from mother to child or a birth defect. Acquired heart block can arise from genetic changes, heart attack damage, muscle disorders, certain surgeries, or medications.
Symptoms of Heart Blockage
People with heart block may experience:
- Shortness of breath
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Cardiac arrest
- Severe tiredness
- Fainting
Diagnosing Heart Blockage
If you experience symptoms of heart block, consult a cardiologist who will review your medical history and recommend diagnostic tests such as:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to check the heart’s structure and function.
- Holter Monitoring: A portable device records a continuous ECG over 24 to 72 hours.
Heart Blockage Treatment
Treatment varies depending on the severity:
- First-Degree Heart Block: Usually does not require treatment.
- Second-Degree Heart Block: May require a pacemaker if symptoms are prominent.
- Third-Degree Heart Block: A pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is often necessary. These devices monitor and send electrical signals to stimulate the heart to beat at a specific rate, becoming active if the heartbeat slows below a predefined level.