Complete Knee Replacement in India: A Comprehensive Guide
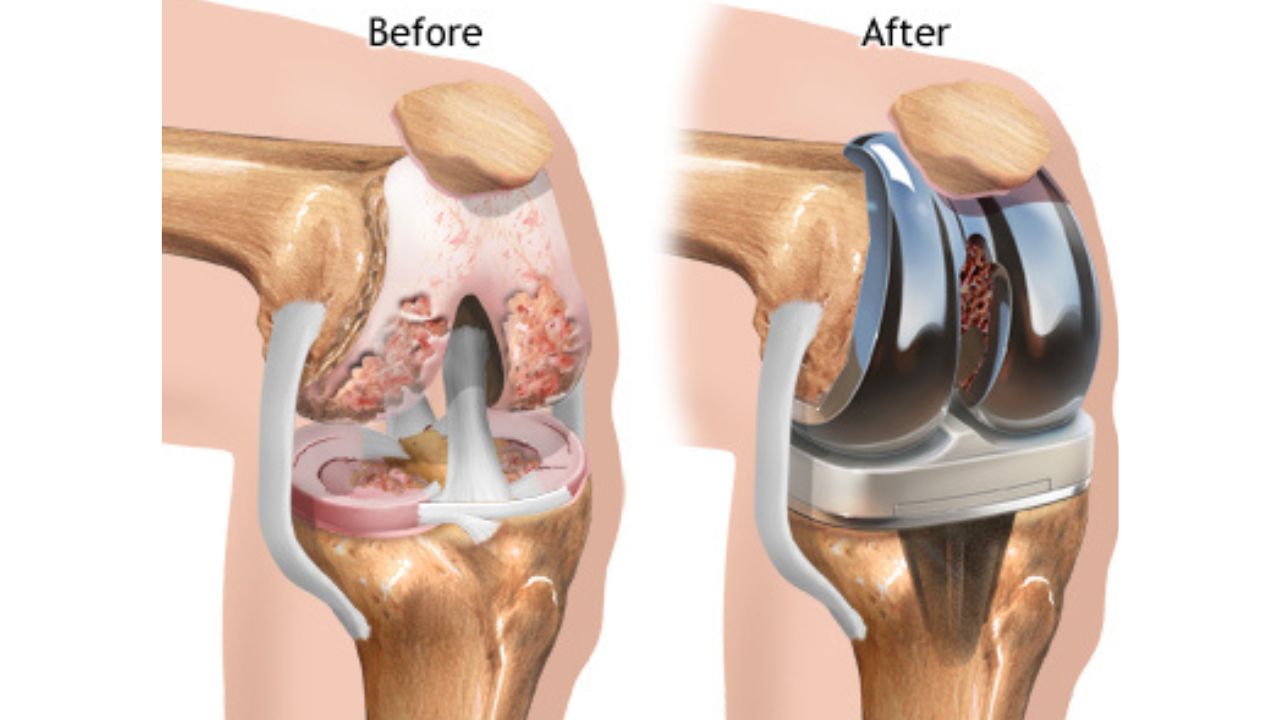
What is Complete knee replacement? Total knee replacement, or knee arthroplasty, involves surgically replacing a damaged knee joint with an artificial prosthesis made of metal and plastic. This procedure is ideal for individuals suffering from severe knee pain and limited function due to arthritis or other joint issues. The surgery aims to alleviate pain, restore mobility, and enhance overall quality of life.
Who Can Benefit from Total Knee Replacement?
Total knee replacement is typically recommended for individuals with chronic knee pain and mobility issues that disrupt daily activities. Osteoarthritis is the most common condition leading to this surgery. This degenerative disease wears down knee cartilage, causing painful bone-on-bone contact. Other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, knee deformities, and severe injuries, may also necessitate this procedure. If conservative treatments like medication and physical therapy fail, total knee replacement becomes a viable solution.
Procedure Overview
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and lasts about two hours. The surgeon makes an incision to access the knee joint. They move the kneecap aside to reach the damaged ends of the thigh and shin bones. After removing the worn cartilage and bone surfaces, the surgeon replaces them with a prosthetic joint. This prosthesis typically includes a metal component for the thigh bone, a plastic spacer to act as cartilage, and another metal or plastic piece for the shin bone. In some cases, bone cement secures the prosthesis, though certain designs allow bone to grow into the implant. The incision is then closed with sutures or surgical clips, and the knee is bandaged. Sometimes, a drainage tube is placed to prevent fluid buildup but is removed within 48 hours.
Recovery Period
After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 3 to 7 days. During this time, a physiotherapist helps with exercises to regain knee function and mobility. Early movement is crucial to avoid complications like blood clots. Patients begin with a walker and progress to crutches or a cane. Full recovery, including pain relief and swelling reduction, can take up to three months. Most individuals can return to work and drive within 4 to 6 weeks, though this can vary based on the patient and their job.
Risks and Complications
Total knee replacement, like any major surgery, has risks. Potential complications include infection, bleeding, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Other risks are tissue damage, nerve injury, or persistent knee stiffness. Occasionally, the prosthesis may loosen or fail, requiring revision surgery. Patients might also experience numbness around the incision, leg length discrepancies, or limited motion post-surgery. Regular follow-ups with the surgeon are essential for monitoring recovery and addressing any issues.
Conclusion
Total knee replacement in India offers a promising solution for those with severe knee pain and mobility issues. With modern surgical techniques and high-quality prosthetics, patients can experience significant improvements. It’s crucial to be aware of potential risks and commit to a thorough rehabilitation process for the best results.