Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) in India
An Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) is a permanent device implanted in a patient’s chest to monitor and manage irregular heartbeats. This device is essential for treating severe arrhythmias, including bradycardia (slow heartbeat), tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), and atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat). AICDs are particularly valuable for patients at risk of life-threatening heart rhythms.
What is an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator?
An Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) is a compact, battery-operated device that continuously monitors the heart’s rhythm. The ICD connects to the heart via tiny wires. When it detects an abnormal heartbeat, it delivers an electrical shock to restore normal rhythm. This process helps prevent sudden cardiac arrest and other severe complications caused by irregular heart rhythms.
How is an AICD Implanted?
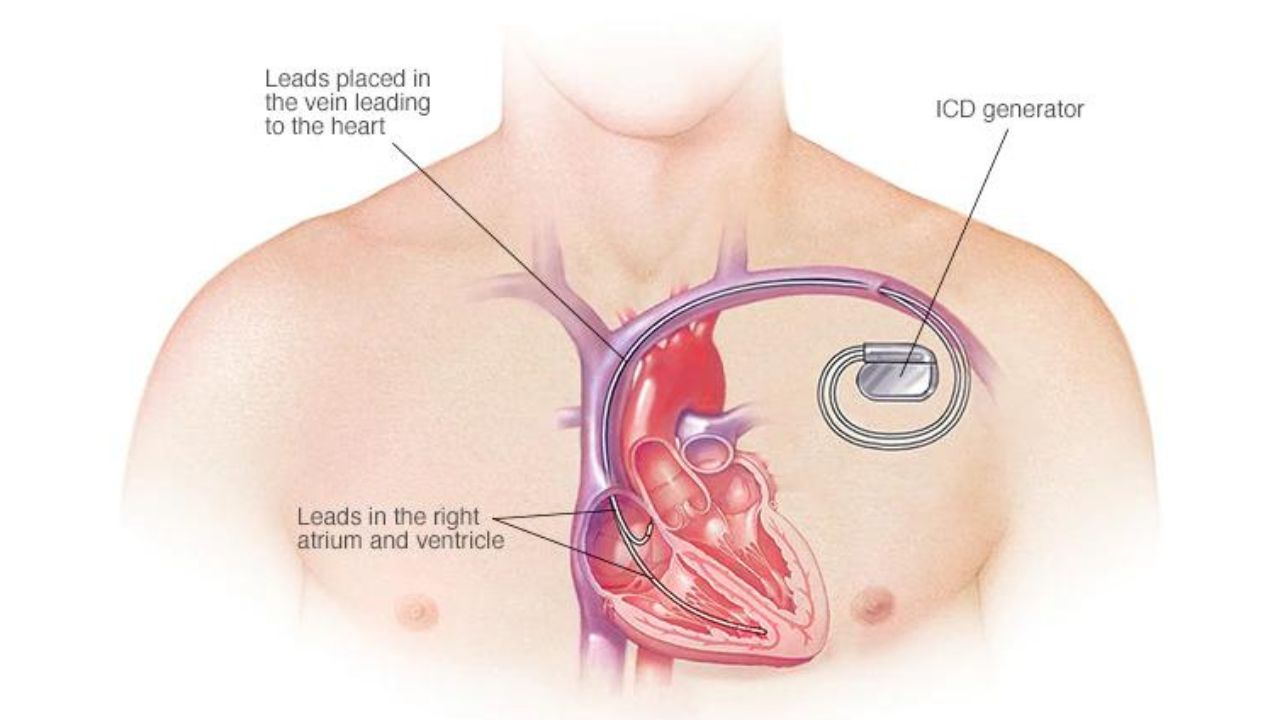
To implant an AICD, a surgeon inserts a pulse generator into a pouch under the skin of the chest, usually near the ribcage or just below the collarbone. The procedure avoids open-heart surgery. Instead, doctors insert leads or wires through blood vessels to connect the generator with the heart. This minimally invasive approach allows for effective monitoring and treatment of arrhythmias.
Goals and Benefits of AICD
The main goal of an AICD is to manage and correct abnormal heart rhythms, which can be fast, slow, or irregular. These arrhythmias can lead to serious health issues, including cardiac arrest. By using high-speed pacing, known as cardioversion, the AICD aims to correct these irregularities. If cardioversion is unsuccessful, the device performs defibrillation to restore normal heart rhythm. As a result, the AICD significantly improves survival rates for patients with severe arrhythmias.
AICD Implantation Procedure
The AICD implantation procedure is similar to that of a pacemaker. The device consists of a generator and electrode leads. Surgeons place the generator under the skin on the upper left side of the chest. They then thread the electrode leads through a vein into the right heart chambers, typically anchoring them in the right ventricular septum. This setup allows the AICD to monitor the heart’s electrical activity and deliver appropriate therapy as needed. Unlike pacemakers, which may be temporary, AICDs are usually permanent devices designed to prevent fatal arrhythmias.
In India, advanced AICD technology offers patients an effective solution for managing severe heart rhythm disorders, enhancing their quality of life and overall survival.