Acute Kidney Injury: Understanding the Condition
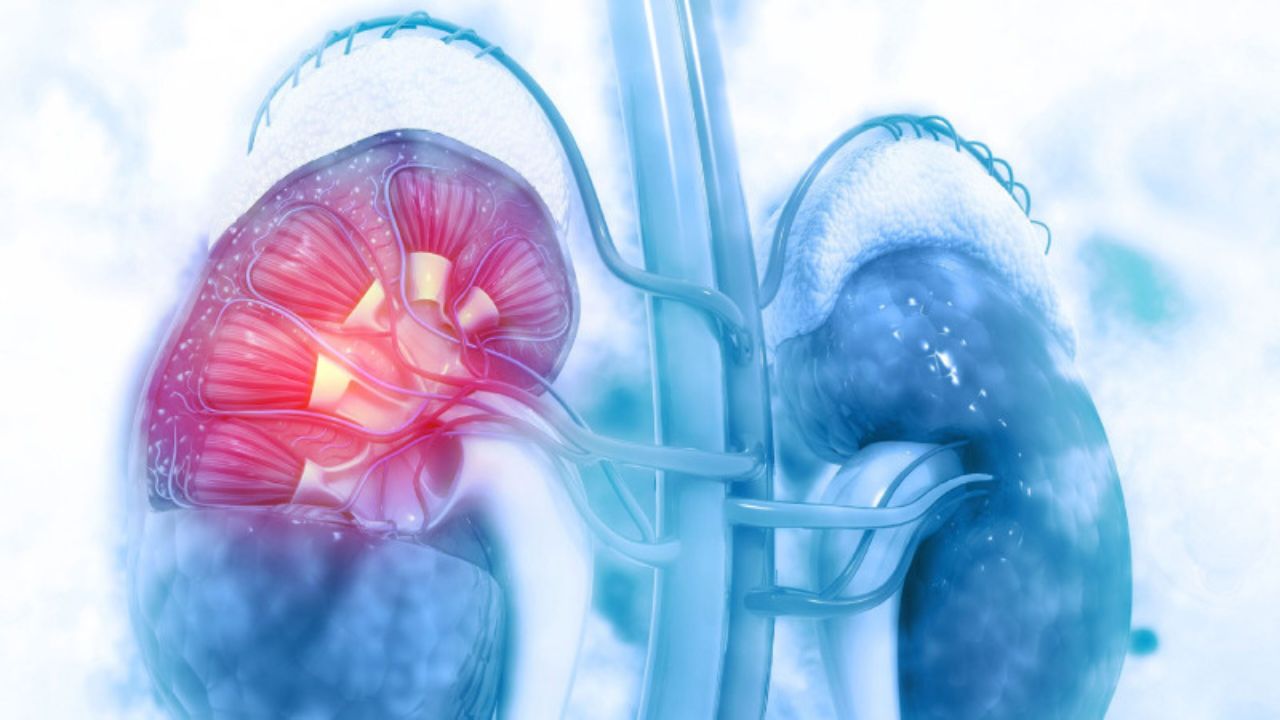
Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurs when your kidneys suddenly lose their ability to filter waste from the blood. This critical function includes removing waste, balancing fluids, regulating blood pressure, and promoting red blood cell production in the bone marrow. When AKI happens, the kidneys become damaged and can no longer perform these essential tasks. The severity can range from a mild decrease in function to complete kidney failure. Despite the name, acute kidney injury is not typically due to a physical trauma but is often caused by severe underlying conditions. Older adults with preexisting health issues are particularly at risk.
Symptoms of Acute Kidney Injury
Initially, symptoms might be subtle or absent. As the condition progresses, you may notice:
- Reduced urine output
- Dehydration
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Elevated blood pressure
- Occasional back pain
- Confusion
- Edema, or fluid retention
Causes of Kidney Injury
The primary cause of AKI is a decrease in blood flow to the kidneys. This reduction can result from:
- Heart failure, leading to reduced blood output
- Liver diseases
- Low blood volume from bleeding, diarrhea, or dehydration
- Blood vessel issues within the kidneys, such as clots or inflammation
- Kidney stones
- Enlarged prostate gland
- Pelvic tumors
- Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Infections, drug allergies, or radiation damage
Risks for Kidney Injury
Several factors can increase your risk of AKI, including:
- Being over 65 years old
- Having pre-existing kidney disease
- Suffering from chronic conditions like heart failure
- Diabetes
- Urinary tract obstructions
- Use of certain medications such as ACE inhibitors, ibuprofen, or diuretics
Prevention Strategies
To lower your risk of acute kidney injury, prioritize a healthy lifestyle. Avoid excessive use of over-the-counter pain medications and adhere to prescribed guidelines. Manage chronic conditions through dietary adjustments and regular, moderate exercise to maintain optimal blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Early diagnosis and management are crucial in preventing complications and preserving kidney function. If kidney injury progresses to complete renal failure, dialysis may become necessary to support kidney function.